前面讲了 select 和 poll 的原理,接下来我们学习它们改进后的增强版本:epoll。
epoll介绍
epoll相关函数
在 man 手册中,可以查到 epoll 的函数原型如下:
1 | int epoll_create(int size); |
具体参数详解:
- epoll_create : 创建 epoll 句柄。
- size : 并没有什么用,但是必须要大于 0,否则创建 epoll 句柄失败。
- epoll_ctl : epoll 事件注册函数。
- epfd : 由 epoll_create 创建的 epoll 句柄。
- op : fd 的操作类型:
- EPOLL_CTL_ADD : 注册新的 fd 到 epfd 中。
- EPOLL_CTL_MOD : 修改已注册的 fd 的监听事件。
- EPOLL_CTL_DEL : 从 epfd 中删除一个 fd。
- fd : 监听的文件描述符。
- event : 要监听的事件,事件属性可以查看下表。
- epoll_wait : 等待 epoll 事件的产生。
- epfd : 由 epoll_create 创建的 epoll 句柄。
- events : 内核得到的就绪事件集合。
- maxevents : 内核events的大小。
- timeout : 设定超时时间:
- 0 : 立即返回。
- -1 : 阻塞。
- 正数 : 设定超时时间。
epoll_event 结构如下:
1 | typedef union epoll_data { |
event 中指定的位掩码的值如下:
| 事件 | 描述 | 是否可作为 epoll_ctl() 的输入 | 是否可作为 epoll_wait() 的输出 |
|---|---|---|---|
| EPOLLIN | 表示对应的文件描述符可读 | √ | √ |
| EPOLLOUT | 表示对应的文件描述符可写 | √ | √ |
| EPOLLRDHUP | Linux 2.6.17 版本后添加的事件,表示对端断开连接 | √ | √ |
| EPOLLPRI | 表示对应的文件描述符有紧急数据可读(外带数据) | √ | √ |
| EPOLLERR | 表示对应的文件描述符发生错误 | × | √ |
| EPOLLHUP | 表示对应的文件描述符被挂断 | × | √ |
| EPOLLET | 采用边缘触发事件通知 | √ | × |
| EPOLLONESHOT | 在完成事件通知之后禁用检查 | √ | × |
工作模式:
epoll 除了提供 select/poll 那种 IO 事件的水平触发(level-triggered)外,还提供了边缘触发模式(edge-triggered),这就是的用户空间程序有可能缓存 IO 状态,减少 epoll_wait/epoll_pwait 的调用,提高应用程序效率。
- 水平触发(LT) : 默认工作模式,即当 epoll_wait 检测到某描述符事件就绪并通知应用程序时,应用程序可以不立即处理该事件。下次调用 epoll_wait 时,会再次通知此事件。
- 边缘触发(ET) : 当 epoll_wait 检测到某描述符事件就绪并通知应用程序时,应用程序必须立即处理该事件。如果不处理,下次调用 epoll_wait 时,不会再次通知此事件。(直到你做了某些操作导致该描述符变成未就绪状态了,也就是说边缘触发只在状态由未就绪变为就绪时只通知一次)。
epoll 工作在 ET 模式的时候,必须使用非阻塞套接字,以避免由于一个文件句柄的阻塞读/写操作把处理多个文件描述符的任务饿死。
epoll使用
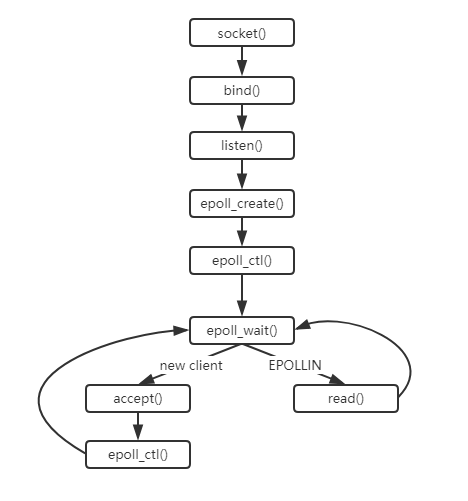
使用流程图如下:
实现简单的服务代码:
1 |
|
epoll实现原理
epoll 的源码也在 fs/eventpoll.c 文件中。
epoll_create()
系统调用宏定义:
1 | SYSCALL_DEFINE1(epoll_create, int, size) |
用户调用 epoll_create 时,检查完 size 参数后,直接调用了 sys_epoll_create1() 函数来完成主要的工作。
sys_epoll_create1() 如下:
1 | SYSCALL_DEFINE1(epoll_create1, int, flags) |
其中,有一个很重要的结构体 eventpoll,其结构如下:
1 | struct eventpoll { |
从上面的结构体中可以看出,epoll 底层两个重要的数据结构是 红黑树 和 单链表的就绪队列,其中红黑树用于管理所有监听的 fd,就绪队列用于将产生了事件的 fd 传回给用户。
那么,创建 epoll 完成后,就需要对文件描述符进行监听、删除、修改等操作,这将会使用到 epoll_ctr() 函数。
epoll_ctr()
系统调用宏定义:
1 | SYSCALL_DEFINE4(epoll_ctl, int, epfd, int, op, int, fd, |
epoll_ctl() 函数支持三种操作:添加、删除和修改,这些操作是基于存储文件描述符的红黑树上的,都是对红黑树进行相应的操作。
接下来我们看看最重要的函数 epoll_wait()。
epoll_wait()
系统调用宏定义:
1 | SYSCALL_DEFINE4(epoll_wait, int, epfd, struct epoll_event __user *, events, |
epoll_wait 的主要工作在 ep_poll() 函数中完成:
1 |
|
ep_poll() 如果有事件发生,则调用 ep_send_events()/ep_scan_ready_list() 将发生的事件拷贝到用户空间中。
1 | static int ep_send_events(struct eventpoll *ep, |