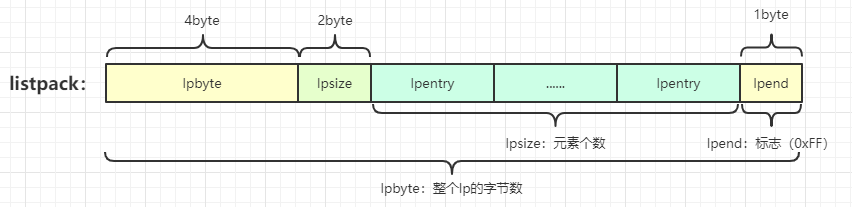
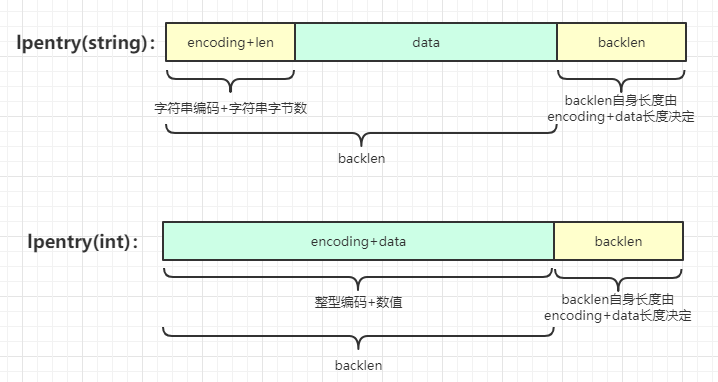
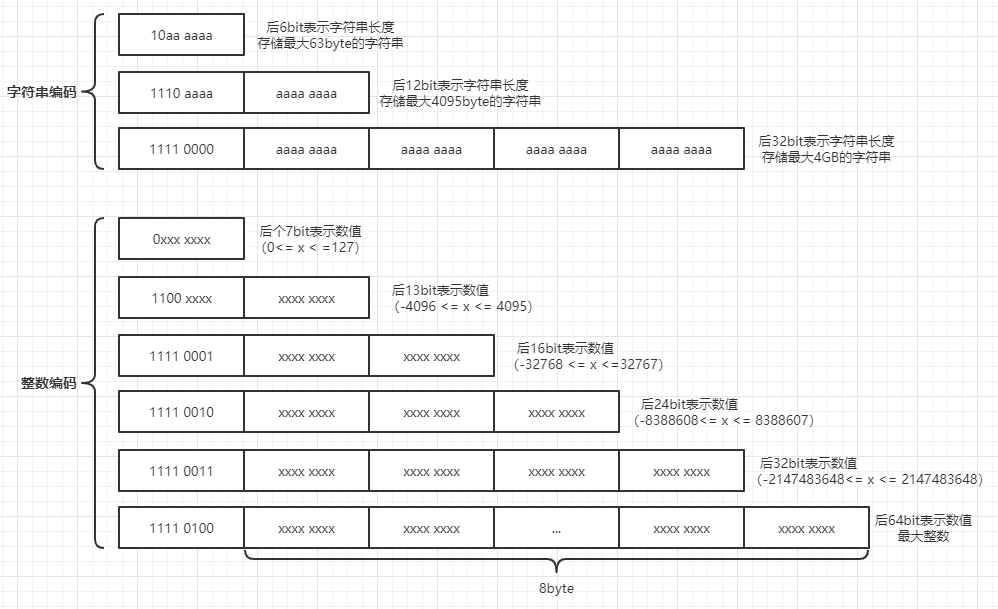
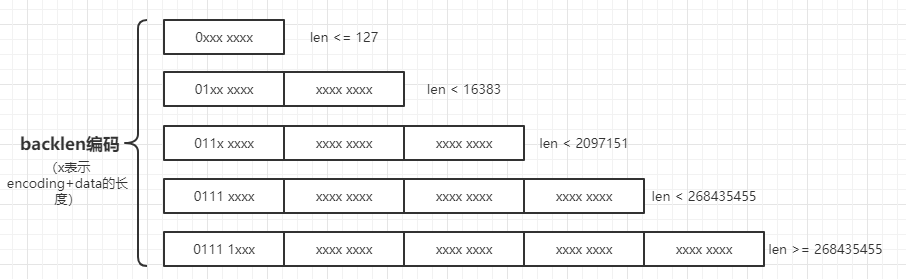
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
|
unsigned char *lpAppend(unsigned char *lp, unsigned char *ele, uint32_t size) {
uint64_t listpack_bytes = lpGetTotalBytes(lp);
unsigned char *eofptr = lp + listpack_bytes - 1;
return lpInsert(lp,ele,size,eofptr,LP_BEFORE,NULL);
}
unsigned char *lpDelete(unsigned char *lp, unsigned char *p, unsigned char **newp) {
return lpInsert(lp,NULL,0,p,LP_REPLACE,newp);
}
unsigned char *lpInsert(unsigned char *lp, unsigned char *ele, uint32_t size, unsigned char *p, int where, unsigned char **newp) {
unsigned char intenc[LP_MAX_INT_ENCODING_LEN];
unsigned char backlen[LP_MAX_BACKLEN_SIZE];
uint64_t enclen;
if (ele == NULL) where = LP_REPLACE;
if (where == LP_AFTER) {
p = lpSkip(p);
where = LP_BEFORE;
}
unsigned long poff = p-lp;
int enctype;
if (ele) {
enctype = lpEncodeGetType(ele,size,intenc,&enclen);
} else {
enctype = -1;
enclen = 0;
}
unsigned long backlen_size = ele ? lpEncodeBacklen(backlen,enclen) : 0;
uint64_t old_listpack_bytes = lpGetTotalBytes(lp);
uint32_t replaced_len = 0;
if (where == LP_REPLACE) {
replaced_len = lpCurrentEncodedSize(p);
replaced_len += lpEncodeBacklen(NULL,replaced_len);
}
uint64_t new_listpack_bytes = old_listpack_bytes + enclen + backlen_size
- replaced_len;
if (new_listpack_bytes > UINT32_MAX) return NULL;
unsigned char *dst = lp + poff;
if (new_listpack_bytes > old_listpack_bytes) {
if ((lp = lp_realloc(lp,new_listpack_bytes)) == NULL) return NULL;
dst = lp + poff;
}
if (where == LP_BEFORE) {
memmove(dst+enclen+backlen_size,dst,old_listpack_bytes-poff);
} else {
long lendiff = (enclen+backlen_size)-replaced_len;
memmove(dst+replaced_len+lendiff,
dst+replaced_len,
old_listpack_bytes-poff-replaced_len);
}
if (new_listpack_bytes < old_listpack_bytes) {
if ((lp = lp_realloc(lp,new_listpack_bytes)) == NULL) return NULL;
dst = lp + poff;
}
if (newp) {
*newp = dst;
if (!ele && dst[0] == LP_EOF) *newp = NULL;
}
if (ele) {
if (enctype == LP_ENCODING_INT) {
memcpy(dst,intenc,enclen);
} else {
lpEncodeString(dst,ele,size);
}
dst += enclen;
memcpy(dst,backlen,backlen_size);
dst += backlen_size;
}
if (where != LP_REPLACE || ele == NULL) {
uint32_t num_elements = lpGetNumElements(lp);
if (num_elements != LP_HDR_NUMELE_UNKNOWN) {
if (ele)
lpSetNumElements(lp,num_elements+1);
else
lpSetNumElements(lp,num_elements-1);
}
}
lpSetTotalBytes(lp,new_listpack_bytes);
#if 0
unsigned char *oldlp = lp;
lp = lp_malloc(new_listpack_bytes);
memcpy(lp,oldlp,new_listpack_bytes);
if (newp) {
unsigned long offset = (*newp)-oldlp;
*newp = lp + offset;
}
memset(oldlp,'A',new_listpack_bytes);
lp_free(oldlp);
#endif
return lp;
}
|